
Dear colleagues,
Welcome to our summer news!
We are pleased to offer you a choice of articles on neuromuscular ultrasound that were published in the second quarter of 2022.
Carpal tunnel syndrome comes with a lot of news as always. Check out about CTS in diabetic patients and scanning before carpal tunnel release. Further a big review on shear wave elastography of nerves and muscles might be of interest for you, as we think it clarifies the need for standardized assessment in neuromuscular ultrasound. The other presented studies are a great mix of different topics.
We hope you’ll enjoy your read.
© Gerlinde Maria Gruber,2019
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME & OTHER ENTRAPMENT NEUROPATHIES
Chao TC et al. The effectiveness of hydrodissection with 5% dextrose for persistent and recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome: a retrospective study. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(13): 3705
This retrospective study looked at the long-term effectiveness of hydrodissection with 5% dextrose for persistent or recurrent post-surgical CTS. 36 patients underwent a structured telephone interview at least six months after treatment. 61% of those reported an effective outcome (defined as over 50% symptom relief after a mean of 3.1 injections and a mean follow-up of 33 months.
The authors conclude that hydrodissection may result in a clinically important and durable benefit in patients with persistent or recurrent CTS.
Heiling B et al. Electrodiagnostic testing and nerve ultrasound of the carpal tunnel in patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J Clin Med 2022; 11(12): 3374
For this study, 69 patients with type 2 diabetes completed the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire, underwent electrodiagnostic testing and nerve ultrasound for assessment of CTS. Of those, only 19 (28%) patients reported predominantly mild CTS symptoms, but 37 (54%) met the criteria for diagnosis of CTS with EDX and 45 patients (65%) had a CSA that exceeded the upper limit normal of 12 mm2.
The authors therefore advise to diagnose CTS in diabetic patients primarily on clinical symptoms.
Saglam G et al. Ultrasonographic measurement of median nerve cross-sectional area in evaluating carpal tunnel release outcomes. J Hand Surg Am 2022; online ahead of print May 6.
CSA of the median nerve at the wrist proximally and distally was measured in 172 wrists before and three months after carpal tunnel release. The mean CSA proximal decreased from 16.4 ± 4.5 mm2 to 12.1 ± 3.9 mm2, the mean distal from 11.0 ± 3.1 mm2. The authors conclude that preoperative mean nerve CSA could be used for evaluating CTR outcomes.
Mansiz-Kaplan B et al. Effect of perineural dextrose injection on ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: a randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2022; online ahead of print Jun 8.
We now already know dextrose injection for carpal tunnel syndrome – so this study went further and tried it for treated 40 patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow with either saline in the control group or 5% dextrose in the treatment group. The total volume was 5 cc, one each at 2 and 4 cm proximal and distal to the medial epicondyle and one at the level of the medial epicondyle. The procedure was performed twice with a 2-weeks`-interval. Patients were evaluated with VAS for pain and Quick-DASH for disability at baseline and at weeks 2, 4 and 12. Improvement in pain, disability, ulnar nerve motor velocity and CSA were superior in the treatment group compared to the control group. Perineural dextrose injection is suggested as an effective alternative therapy in patients with ulnar neuropathy at the elbow for up to the week 12.

NERVE TRAUMA
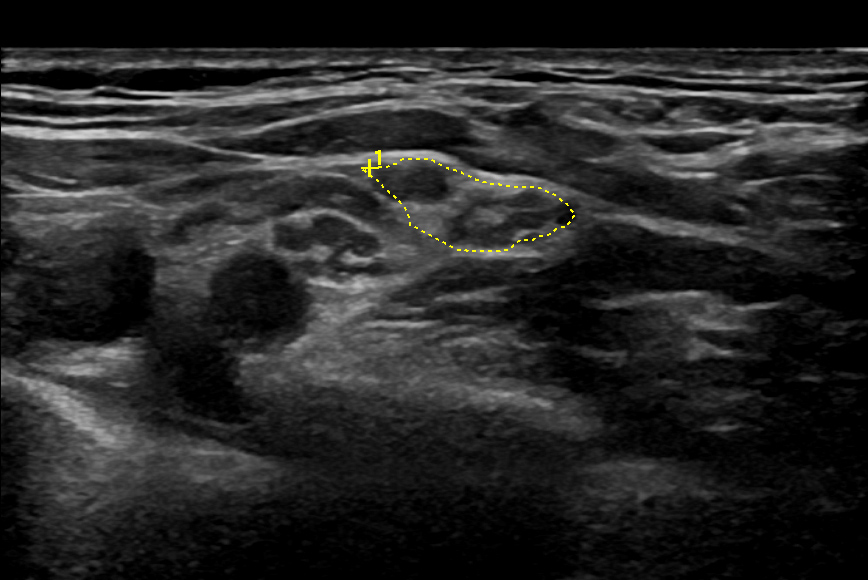
Leonardi L et al. Nerve high-resolution ultrasound in a 2-years follow-up of radial nerve palsy related to humeral shaft fracture. J Neurosurg Sci 2022 Jun 28; online ahead of print
In this study, 19 patients with humeral shaft fracture and associated radial neuropathy were followed up for 2 years with electrodiagnostics and HRUS.
HRUS proved anatomical nerve continuity in all patients and PIN involvement in74%. The CSA of the radial nerve progressively reduced during follow-up, but stayed significantly larger than on the healthy side.
EDX functional continuity was reached in all patients within 12 months. The authors concluded that prognosis of radial neuropathy after humeral shaft fracture is good, even in patients with initial loss of functional continuity.
POLYNEUROPATHY
Abdelnaby R et al. Nerve sonography in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 6061 measured nerves. Ultrasound Med Biol; epub Jun 3.
This meta-analysis presents the pooled measurements of nerve CSA in 628 patients with CMT and 586 controls from studies published in international peer-reviewed journals. Asssessed nerves include: vagus, C3, C4, C5, C6, greater auricular, phrenic, median, ulnar, fibular, tibial and sural nerves.
*Erdmann et al. Nerve echogenicity in polyneuropathies of various etiologies – results of a retrospective semi-automatic analysis of high-resolution ultrasound images. Diagnostics 2022; 12(6): 1341
This study aimed at analyzing and comparing nerve echogenicity of patients with critical illness polyneuropathy (n=19), chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy (n=27) and CIDP (n=20). Ultrasound images were converted to black and white and fraction of black defined. Overall, differences were slight and cannot be used for differentiating between polyneuropathies. Patients with progressive CIDP (n=8/20) showed significant hyperechogenicity of the median nerve at the forearm and upper arm and the ulnar nerve at the upper arm, which might be interesting for future research.
Oka Y et al. Nerve ultrasound characteristics of immunoglobulin M neuropathy associated with anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibodies. Muscle Nerve 2022; 65 (5): 667-75
A small and retrospective study that compared CSAs of C5-7 cervical roots, median and ulnar nerves of 6 IgM/anti-MAG neuropathy patients, 10 patients with typical CIDP, 5 patients with multifocal CIDP and 17 healthy controls.
They found enlargement of roots on both sides and nerves at classical entrapment sites in the IgM/anti-MAG group comparable to the enlargement in typical CIDP, but larger than in multifocal CIDP. The authors suggest further studies on these subtypes.
ELASTOGRAPHY
Cipriano KJ et al. A scoping review of methods used in musculoskeletal sofot tissue and nerve shear wave elastography studies. Clin Neurophysiol 2022; online ahead of print April 30
Shear wave elastography is one of the emerging topics in neuromuscular and musculoskeletal ultrasound. This study summarizes the currently available literature for examination of skeletal muscles, tendons and nerves with this technique. Of 5868 published papers, only 375 fulfilled inclusion criteria, among them 260 examining muscles, 94 tendons and 43 nerves. Identified problems were: small and young cohorts, a variety of ultrasound systems, models and transducers, missing confirmation of muscle activity by EMG (89% of studies) and missing information about measurement depth (92% of studies).
The authors pleaed for standardized SWE collection and reporting procedures to further advance diagnostic impact of the method in reporting of tissue pathology, disease progression and response to intervention.

MUSCLE ULTRASOUND
Wijntjes J et al. Visual versus quantitative analysis of muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disease. Muscle Nerve 2022 Jun 28; online ahead of print
For this study, the authors reviewed 13562 muscle ultrasound images of 994 patients and compared echogenicity z-score distribution to grading with the Heckmatt scale. The two scoring systems showed only a moderate correlation of 0.60. Discrepant scores were rare (<2%). The authors concluded that these two scores should be used as complementary techniques.
van Doorn JLM et al. Association of diaphragm thickness and echogenicity with age, sex, and body mass index in healthy subjects. Muscle Nerve 2022; online ahead of print May 18.
This study looks at the influence of age, sex and body mass index (BMI) on the most important ultrasound measurements of the diagphragm (thickness at resting end-expiration, maximal end-inspiration and diaphragm thickening ratio) as well as diaphragm echogenicity. They examined 83 healthy subjects and found no correlation between age and respiratory measurements, but echogenicity increased. End-exspiration thickness was positively correlated with BMI and men exhibited a larger diaphragm thickness at end-expiration and maximal end-inspiration, but thickening ratios were similar between the sexes. It was therefore suggested that subject characteristics should be considered when interpreting diaphragm ultrasound measurements. As normative values are missing, matched control groups are required.

SMALL NERVES
Abdelnaby R et al. Sonographic reference values of cranial nerve size: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Muscle Nerve 2022 Jun 28; online ahead of print
The authors reviewed 14 studies with 661 participants and 1437 nerve measurements of the facial, spinal accessory and hypoglossal nerve. The mean nerve diameter was 0.80 mm for the facial, 0.63 mm for the spinal accessory and 1.82 mm for the hypoglossal nerve.
THE INTERESTING CASE
Heinzel J et al. Multihit injury of theradial nerve in a 62-year-old woman: a case report
The authors present a case of a woman who suffered a fracture of the left humerus with subsequent paralysis of all radial innervated muscles except the triceps and a sensory deficit corresponding to the posterior nerve of the forearm and the superficial radial nerve. After initial neurolysis at humeral level, the patient first experienced a re-innervation stop at posterior interosseus level that was solved by decompression at supinator level and a second re-innervation stop at the level of the superficial radial nerve, which was treated by decompression at wrist level.
Ok… now that was a lot to go through. We hope you liked our new and can use some of the information for yourself. If you have any comments or we missed your most important paper, just leave us a comment!
Stay safe, see you soon.
Your Sonocampus Team.

Recent Comments